Laboratoire Epigénétique et destin cellulaire (EDC) :
Equipe Dynamique Epigénétique et Différenciation Cellulaire
http://parisepigenetics.com/edcd/
http://parisepigenetics.com/edcd/
Slimane AIT-ALI, Bertrand COSSON, Véronique JOLIOT, Laurence DELMAESTRO, Costas BOUYIOUKOS, Alice GRANADOS
Epigénétique, Méthylation des Histones
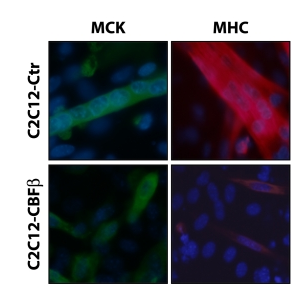
Image de Philipot et al, PlosOne 2010
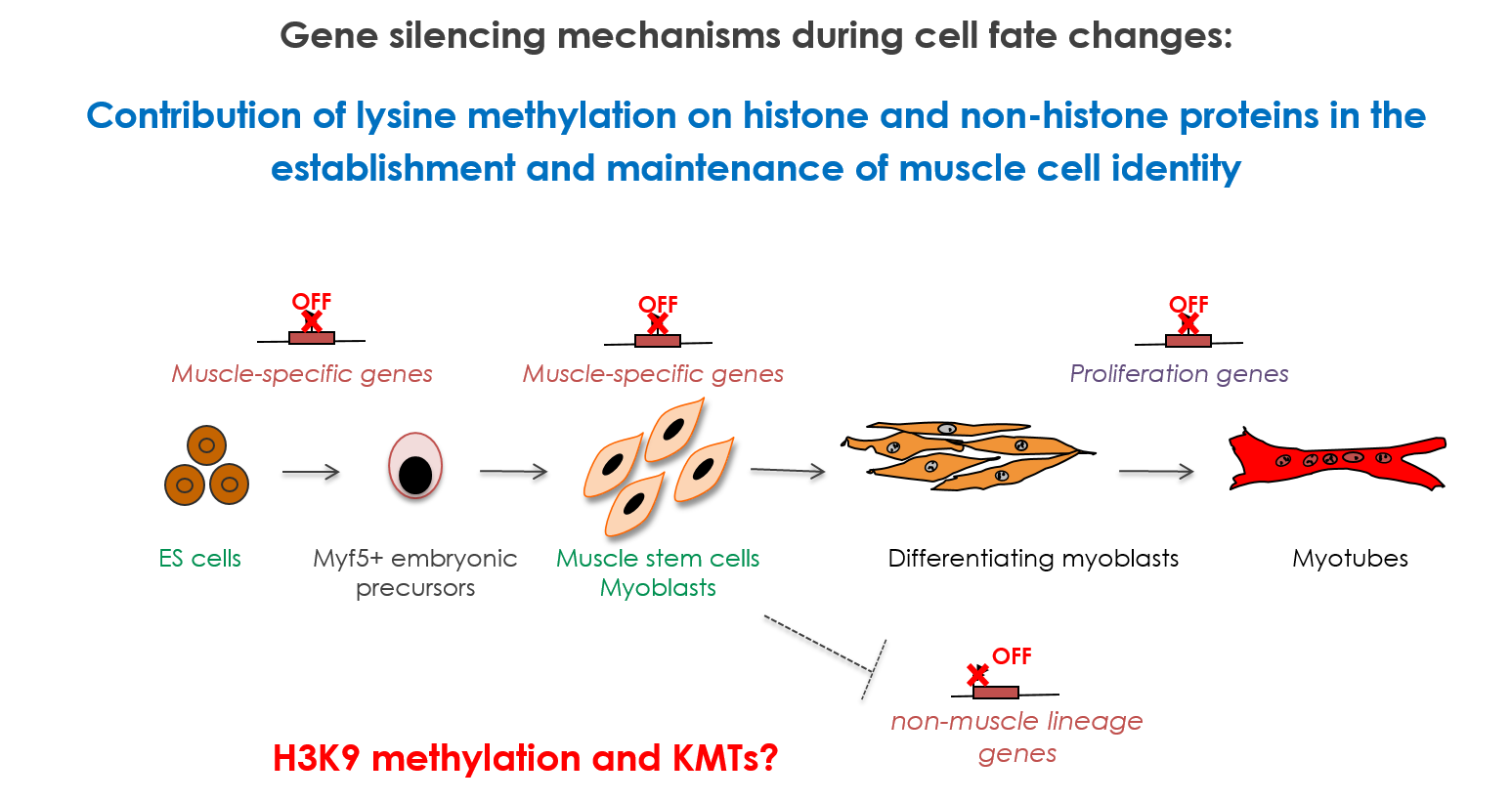
Lysine methylation on histone and non-histone proteins in the establishment and maintenance of cell identity :
Lysine methylation/demethylation of histones is a key epigenetic mechanism. Lysine methylation on histones is associated with both active and inactive domains of chromatin, depending on the residue that is targeted. Methylation of histone H3 on lysine 9 (H3K9) is a hallmark of repressed chromatin. Our group seeks to define the biochemical and molecular mechanisms that govern the H3K9-induced silencing of genes during normal and pathological skeletal muscle differentiation.
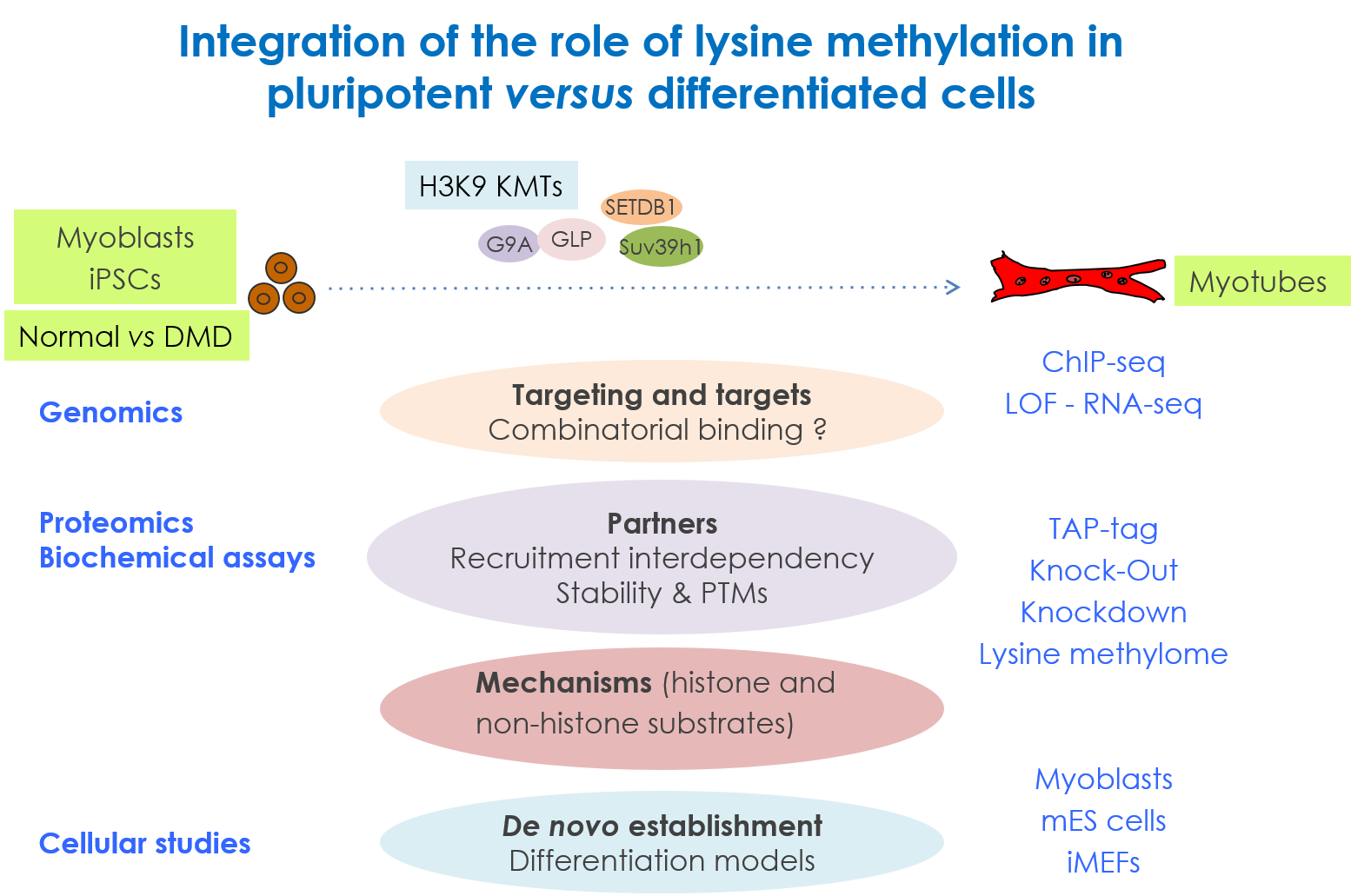
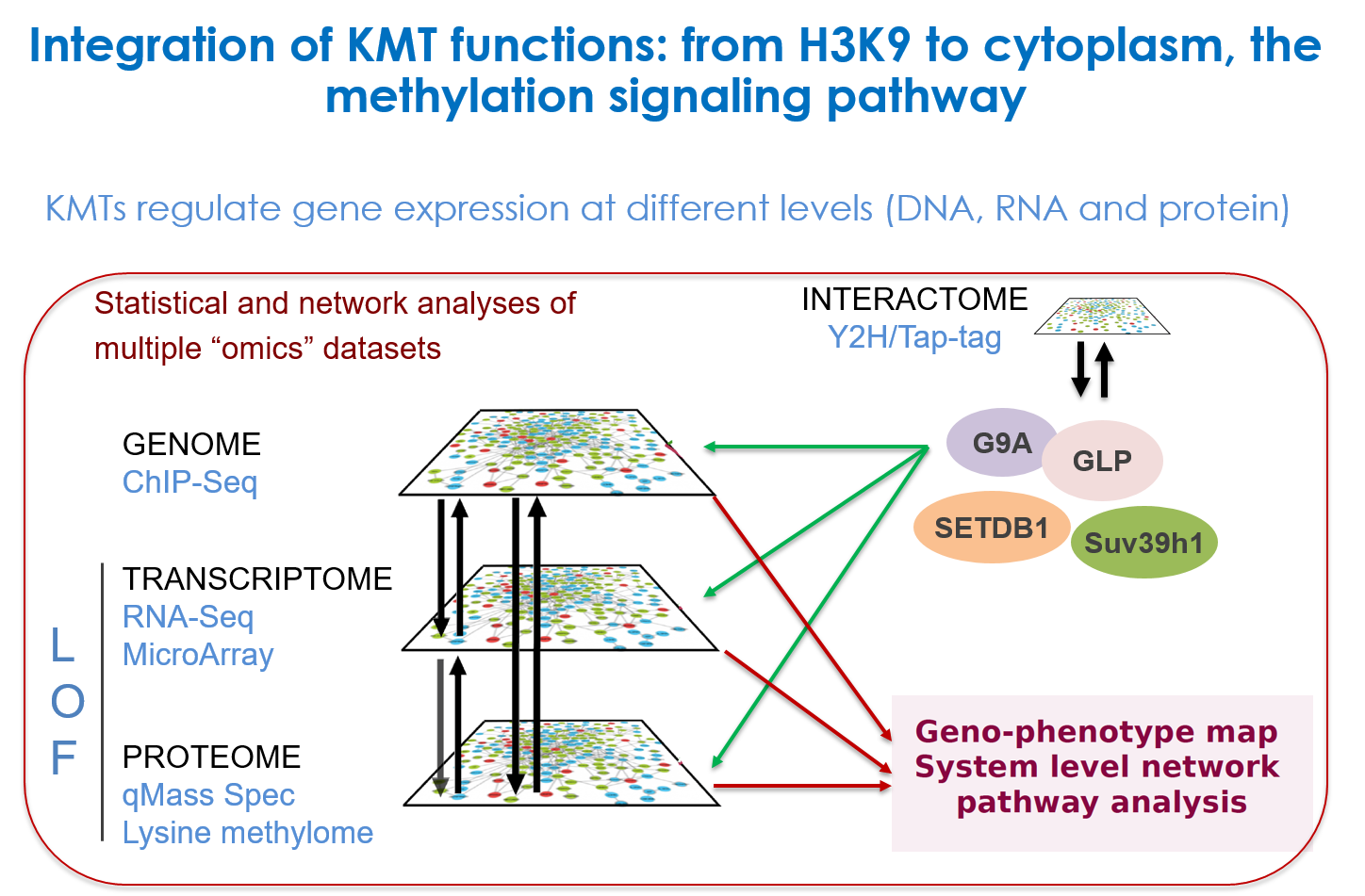
We are interested in the role of H3K9 methylation, as well as methylation of non-histone proteins by the H3K9 lysine methyltransferases (KMTs), in the regulation of muscle and embryonic stem cells (ESCs) differentiation: how the different H3K9 methylation levels (mono, di and tri), associated to specific nuclear compartments, are established in the cell, and how H3K9 KMTs (co)-regulate the cell fate changes. We try to dissect the composition, mechanisms, the kinetic of action of these KMTs and the signaing pathways targeting them (TGFβ and Wnt). Unravelling the molecular mechanisms by which stem cells undergo cell fate decisions, especially differentiation, is one of the fundamental goals of modern medicine. The ability to modify a cell state is a fundamental issue that hold great promises for regenerative medicine. Thus, the expected results will improve our knowledge on the mechanisms governing chromatin modifications during cellular reprogramming, used as a tool in cellular therapy.
Experimental approaches: we combine gain- and loss-of-function, genomic (ChIP-seq, RNA-seq) and proteomic (TAP-tag/Mass spec) approaches to study KMTs at the molecular and cellular levels. As cellular models, we use normal and patient derived myoblasts, and iPSC-derived skeletal muscle cells.